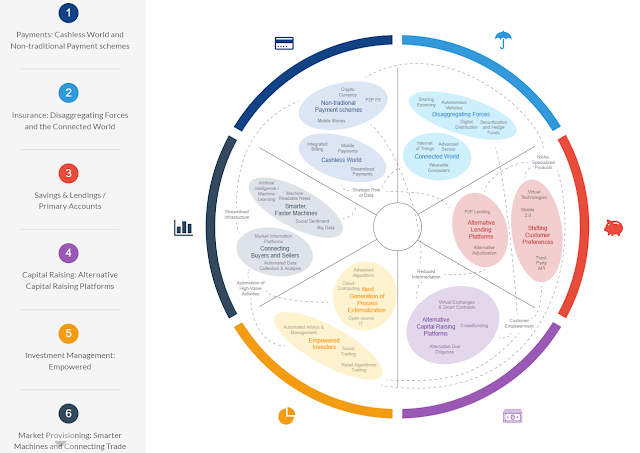
The competition among financial service providers forces them
to reduce the cost of their services and at the same time improve the customer
satisfaction and convenience. In order to achieve the improved business performance,
the banking industry has been relying on Artificial intelligence powered by big
data and machine learning aka Data Science.
According to world economic forum this is where financial services are
going and what technologies will enable the financial institutions to provide
these services.
Figure 1 Forum, W.E. (2016) Future of
Financial Services. Available at: Source
(Accessed: 13 June 2016).
What is central to all these sub sectors? All of them need
to make use of data analysis in some way or the other.
Day by day new companies are entering the financial market
with innovative solutions relying heavily on Data analysis. As discussed in our
previous blogs in the series, the biggest threats and challenges these companies
pose for the traditional financial industry players are:
- Sub-sector Boundaries are blurring – The newer products from these innovative entrants are creating competitive pressure across sub-sectors. Phenomenon like alternative lending, crowdfunding and robo-advisors like betterment.com are challenging the retail banks and taking their customers away.
- Customer ownership is lost – Traditionally, financial institutions relied on bundled services. But the emergence of these niche providers encourages customers to shop around. Moreover, the technology oriented firms offer amazing digital experiences, which is a preferable choice for most specially the youngsters.
- Customer behaviour is changing – With all these online options the customers have a wider mix of options available to choose from. Young adults are taking control of their finances and want the best experience from their financial services providers at a minimum cost. If you can not provide what they want, they will be happy to switch.
Given these challenges, the traditional financial institutions
also have an opportunity. The traditional institutions can also leverage the
use of Data science in their operations and use the data from both on-grid as
well as off-grid channels such as social media to provide on par services to
their customers. The early adopters are already reaping the benefits of big
data. As per a recent global CIO survey conducted by CSC (CSC, 2014), 72%
respondents from financial services sector said that Big Data had a positive
impact on their rate of innovation and 77% believe that Big data has improved their
productivity and efficiency.
The figure below shows the emerging application areas where
financial sector now is using data science to provide better services and
improve business performance.
Source: Frost & Sullivan, (2016), AI impacting Banking
& Financial Services Overview [ONLINE].
Available at source
[Accessed 13 June 2016]
These threats and opportunities balance the future landscape
of the financial services. It also means that it is unlikely that this
landscape will be populated by many outright winners or losers per se. Rather, companies
will be collaborating with each other to help themselves and others, especially,
in fraud detection and prevention – which is a huge priority for the sector. It
is possible that we may be seeing a new platform that aggregates information
from entire industry and find trends and patterns in fraud. Thus if a new treat
or scam appears all the banks can be informed immediately so that the risk of
multiple banks seeing the same frauds will be mitigated immediately and that
too without each of them investing separately in the infrastructure to make
this happen.
Despite all the positive influence there are challenges that
are common to all financial players looking to implement a big data strategy.
One of the key challenge for big data is getting quality data, Banks although
have wealth of data most of this data is kept in silos within different
divisions. Making a central data repository or as some experts say, “Data mart”,
is challenging as it requires integration within old legacy systems. This is
time consuming and expensive. The other challenge that banks face is that most
of the big data strategies have cloud as their infrastructure platform.
Financial institutions in particular are hesitant about bringing their data to
cloud as the regulators keep a tight check on them. Thus understandably, banks
prefer to err on the side of caution. But as the cloud services evolve and get
more secured, this can change very soon. One challenge that financial industry
luckily does not face is getting the right people to get insights from data.
Although, they have the right people to do it, it is expensive for the banks to
keep employing them.
Some of the biggest banks are already testing their newer
applications on cloud. For example, a consortium of major world banks including
JP Morgan Chase, BofA Merrill Lynch, BNY Mellon, BlackRock, Citadel, Citi,
Credit Suisse, Deutsche Bank, Goldman Sachs, Jefferies, Maverick, Morgan
Stanley, Nomura and Wells Fargo recently invested in a venture called Symphony
to provide secure, cloud based communication platform (LLC, 2014).
With all that said, it is evident that Data science is going
to be integral to a banks digital strategy for all major innovations and operations.
As the DBS bank CEO Piyush Gupta says on his digital strategy, (Tan, 2014)
“That is actually going to make the difference between the banks that will
survive and the banks that will not survive”.
Bibliography:
Frost & Sullivan (2016) Artificial Intelligence
Empowering Digital Banking and Finance Ecosystem-IT, Computing and
Communications. Available at:
http://cds.frost.com.proxy.library.cmu.edu/p/55399/#!/ppt/c?id=D881-00-03-00-00&hq=data%20science%20finance
(Accessed: 13 June 2016). In-line Citation:(2016)
CSC (2014) Big data - CSC global CIO survey: 2014–2015.
Available at:
http://www.csc.com/cio_survey_2014_2015/aut/115261-big_data_csc_global_cio_survey_2014_2015
(Accessed: 13 June 2016).In-line Citation:(CSC, 2014)
World Economic Forum (2015) Future of Financial Services.
Available at:
http://reports.weforum.org/future-of-financial-services-2015/executive-summary/?doing_wp_cron=1465787851.6013619899749755859375
(Accessed: 13 June 2016). In-line
Citation:(2015)
LLC, S.C.S. (2014) Press release. Available at: https://symphony.com/press_releases/item/consortium-leading-financial-firms-invest-new-communication-workflow-platform
(Accessed: 13 June 2016).In-line Citation:(LLC, 2014)
Tan, J. (2014) Piyush Gupta demands A shift to digital
banking in Singapore. Available at:
http://www.forbes.com/sites/forbesasia/2014/06/04/piyush-gupta-wants-a-shift-to-digital-banking-in-singapore/#728fe5f14d09
(Accessed: 13 June 2016).In-line Citation:(Tan, 2014)